Deploy an Astro app (SSR)
Introduction
In this guide you will learn how to Dockerize and deploy your Astro app with SSR (server side rendering) in Docker Deploy.
For more info on SSR in Astro, read the official docs.
Pre-requisites
Before starting this guide, make sure you have:
- A running Astro app
- An account on Docker Deploy
Add SSR support
If you have already installed the Node adapter, you can go to the next step
In the root of your project, run:
npx astro add nodeThis will add the needed dependencies and update your configuration to support SSR.
By default, your app will render all your pages in the server at runtime. If you want to pre-render some pages, you can find more information here.
Dockerize your app
If you can already build a docker image for you app, go to the next step
This guides follows the official docs
In the root of your project (where package.json is), add the following files:
Dockerfile
FROM node:lts-alpine AS runtimeWORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN npm installRUN npm run build
ENV HOST=0.0.0.0ENV PORT=4321EXPOSE 4321CMD node ./dist/server/entry.mjsand .dockerignore
.DS_Storenode_modulesdistThese two files will allow you to build a Docker image for your Astro app.
Build and Deploy with the CLI
Instal the CLI
Run npm i dockerdeploy-cli -g to install the CLI in your PC.
Then run dd-cli login to log in your user in the CLI.
Build and Deploy
You can run dd-cli build to build your docker image and push it to your private repository.
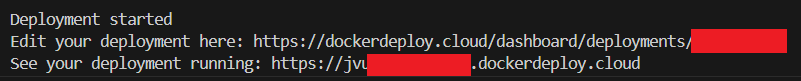
Afterwards, you just need to run dd-cli deploy to deploy the image that you just build into Docker Deploy.
After deploying, you will get the URL to manage that deployment and the automatically generated URL.
Adjust the port
By default, the deployments created through the CLI will listen to the port 80 of your app, but Astro exposes port 4321 by default. So you have to go to you deployment in the dashboard, and change the ports section as follows:
ports: - "80:80"to
ports: - "80:4321"Ready!
You can now visit your site under the autogenerated dockerdeploy.cloud URL!